This week's chapter is mainly a reading chapter, it does need much discussion, so just a few points are explained to avoid repetition.
This chapter begins by comparing the subject of software engineering to other engineer disciplines. The point is made that the lack of quantitative measures of software properties dictates a subjective nature in software engineering that is not present in other disciplines. The chapter then turns to a discussion of the software life cycle and the benefits that can be gained through a good software design. With this background, the chapter discusses issues of modular design (coupling and cohesion), software development tools and techniques (CASE tools, top-down versus bottomup design, design patterns, component architecture, open-source development, structure charts, UML, dataflow diagrams, entity-relationship diagrams), and documentation (user versus system). The chapter closes with a discussion of the problems involved when traditional copyright and patent laws are applied to software.
An important thread that runs through this chapter is the impact that the object-oriented paradigm is having on the subject of software engineering. Indeed, software engineering is more dynamic than ever as it struggles to provide methodologies based on the object-oriented, rather than the imperative, paradigm.
About TC Lite
You should have installed this last week.
The Borland Turbo C / TCLite IDE is a software package which provides an integrated development environment to assist programmers in developing C or C++ programs. In this, IDE integrates editor, compiler, linker, debugger, and other necessary development tools into a single environment. The editor is the starting point. From it, one can request the compile, link, execute operation, or all of them. When everything is done, you are always back at the editor.
- Start the turbo C / TCLite IDE using one of the method that works best for you.
Locate the folder where you installed it, most likely c:\tclite, in c:\tclite\bin directory and execute tc.exe
- If the TC IDE is displayed as below, then create a new program file with File | New.
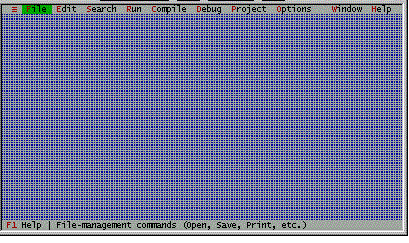
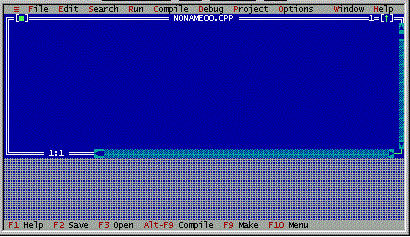
- If the TC IDE screen shows as below, then you are ready to start creating your first C++ program.
The Turbo C / TCLite IDE Components
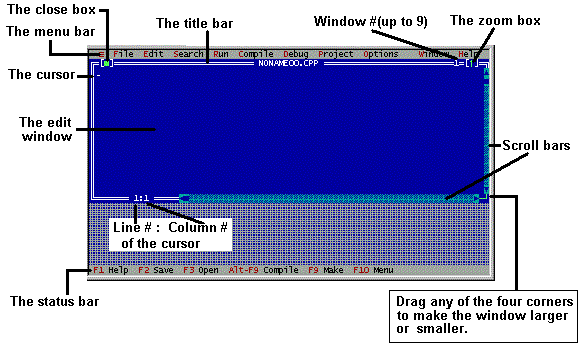
The edit window is where you type your program. The cursor moves while you type your program statements and its positions in line and column are shown at the bottom of the edit window.
The close box of a window is the box in the upper left corner. Click this box to quickly close the window. (Or choose Window | Close.)
The title bar, the topmost horizontal bar of a window, contains the name of the window and the window number. Double-clicking the title bar zooms the window. You can also drag the title bar to move the window around.
The zoom box appears in the upper right corner of the window. In the above screen, the window is in regular size. Click it to zoom the window to the maximum size. Click it again to return the window back to the normal size
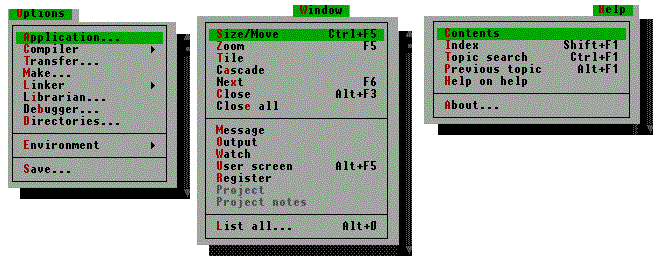
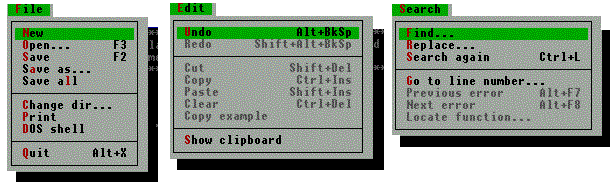
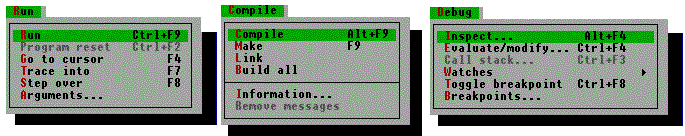
The Menu Bar and Submenus
The IDE menu bar:
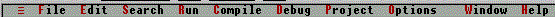
The submenus:
The Edit Window
The edit window is where you type your program. It is possible to work on more than one program with each program in its own edit window. The maximum number of edit windows opened at any one time is nine.
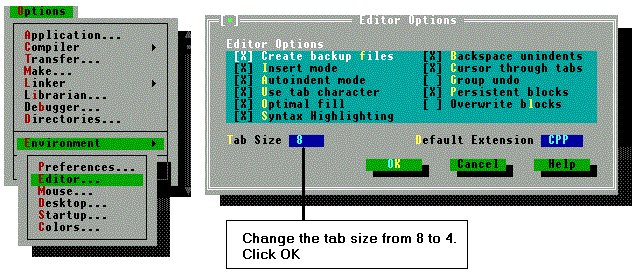
Changing the tab space of the edit window
The default tab space is 8. You can change it to 4 with the following steps:
- Select Options | Environment | Editor... to open the Editor Options window.
- Change the tab size to 4 and click OK.
If you have issues when compiling your programs, with messages such as "can not find include file iostream.h", do the following:
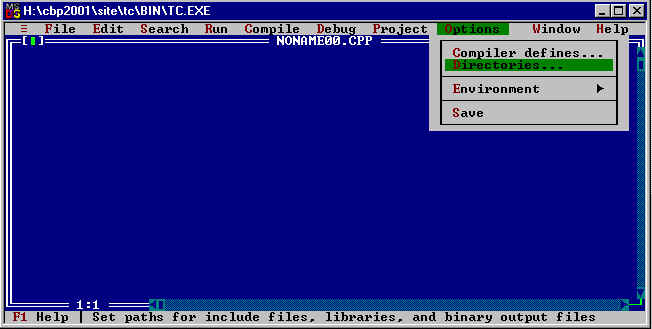
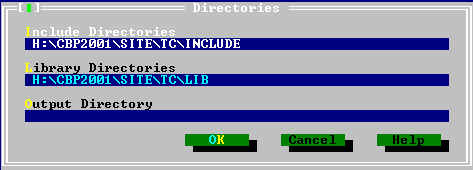
Click on Options and and Directories...
Change the directories according to the settings of your computer:
Implement this program using the TC development environment for practice before you start the actual program.
The bulleted items are not to be included in the code.
Once the code is typed, select the option run, this will execute all the required steps to create the EXE file.
Introduction to C++ Programming Environment
- Identification Comments
// basicpgm.CPP
// Sample program to demonstrate basic C++ program structure
// J.Eleanore Snaird - 6 Sept. 2002
- Preprocessor Directives
#include <iostream.h> // for cin & cout
#include <conio.h> // for clrscr() & getch()
- Start of main Function
void main (void)
{
- Body of main Function
(this is the part that will vary the most)
int shoeSize, age; // define input variables
int estimatedIQ; // define calculated value variable
clrscr(); // erase anything left over on the output window
cout << "Enter your shoe size: ";
cin >> shoeSize;
cout << "Enter your age: ";
cin >> age;
estimatedIQ = (shoeSize*14) - (age*3);
cout << "Your estimated IQ is "
<< estimatedIQ << endl;
cout << endl << endl << "Hit any key to quit";
getch(); // pause until key is typed
- End of main Function
}
C++ help